WIS-SIMS Research Center for Tissue Regeneration
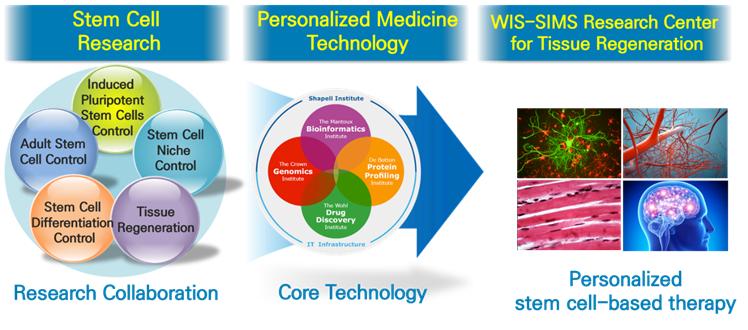
Founded in 2016 as a joint research center of the Israel Weizmann Institute of Science (WIS) and Soonchunhyang Institute of Medi-bio Science (SIMS), the world-class research infrastructure of the WIS in the stem cell field has been intimately fused with the research manpower of SIMS to 1) establish a patient-specific analysis infrastructure to treat incurable and intractable diseases and ultimately 2) develop original stem cell-based therapies and conduct research on tissue regeneration.
□ Overview
○ Project: Global research and development center
○ Director: Prof. Jeong Kyo Yoon
○ Research period: August 10, 2016 ~ January 9, 2022
○ Supported by: Ministry of Science and ICT (National Research Foundation)
□ Central goal

○ The researchers of SIMS and WIS conduct mutually complementary joint research in tissue regeneration and stem cells to discover common areas (Step 1)
○ Based on the discovered common areas, the researchers focus on joint research regarding tissue regeneration and stem cells, and use the world-leading customized medical research infrastructure of WIS (Step 2)
○ Ultimately, through this joint research, we aim to secure original technology in the area of tissue regeneration treatment based on stem cells and lay the foundation for leading the global market (Step 3)
□ R&D achievements
○ Identified the molecular biological mechanisms that regulate the function of muscle stem cells and secured the original technology for advanced culture methods
○ Investigated the cause of Parkinson’s disease using stem cells derived from Parkinson’s patients
○ A study was conducted to compare the metabolic characteristics of pluripotent stem cells with those of intracellular organelles, leading to the discovery that pluripotent stem cells maintain morphologically/structurally immature endoplasmic reticulum as well as mitochondria.
○ Development of various in vitro drug testing platforms in the human hindbrain environment by using brain-specific serotonin neurons and hindbrain organoids




